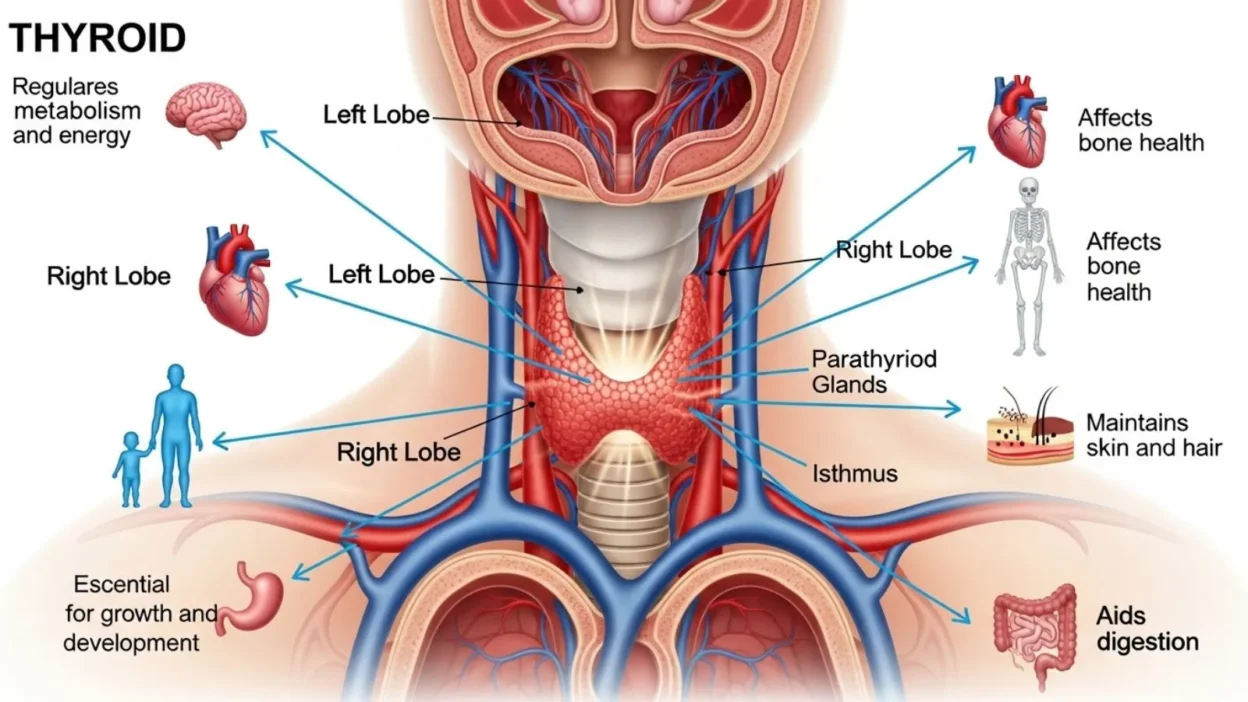
Your thyroid may be small, but it plays a mighty role in your overall health. This butterfly-shaped gland, located at the front of your neck, produces hormones that regulate nearly every system in your body.
From controlling your metabolism and energy levels to influencing your heart rate, mood, and even brain function, the thyroid is a true powerhouse.
When it’s working properly, you may not even notice it but when it’s out of balance, it can lead to a range of symptoms, from fatigue and unexplained weight changes to hair loss and mood swings.
Understanding what your thyroid does and how it affects your body is essential for maintaining long term health.
In this article, we’ll explore the thyroid’s function, signs of imbalance, causes of thyroid problems, and practical ways to support this vital gland so you can feel energized, balanced, and in control of your well-being.
Understanding the Thyroid
The thyroid is a small, butterfly-shaped gland located at the front of your neck, just below the Adam’s apple. Despite its modest size, it has a huge impact on your health because it produces hormones that regulate almost every system in your body. The two main hormones produced by the thyroid are T3 (triiodothyronine) and T4 (thyroxine). These hormones travel through your bloodstream and influence how your body uses energy, maintains temperature, and performs vital functions.
Your thyroid works closely with the pituitary gland, which releases thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) to tell the thyroid how much hormone to produce. This precise feedback system ensures your metabolism stays balanced. When thyroid hormones are at the right levels, your heart rate, digestion, brain function, and energy production all function optimally.
An underactive thyroid (hypothyroidism) produces too little hormone, leading to fatigue, weight gain, and cold intolerance. An overactive thyroid (hyperthyroidism) produces too much hormone, causing rapid heartbeat, anxiety, and weight loss. Beyond metabolism, thyroid hormones also support growth, development, and mood regulation, showing just how essential this gland is to overall health.
Understanding your thyroid and how it affects your body is the first step toward recognizing signs of imbalance and taking proactive steps to support its function. In the following sections, we’ll explore the symptoms, causes, and ways to maintain a healthy thyroid.
Signs and Symptoms of Thyroid Imbalance
Your thyroid influences almost every system in your body, so when it’s not functioning properly, the symptoms can be widespread and sometimes subtle. Hypothyroidism, or an underactive thyroid, occurs when the gland doesn’t produce enough hormones. Common signs include persistent fatigue, unexplained weight gain, dry skin, hair thinning, constipation, and feeling unusually cold. Mood changes such as depression, irritability, or “brain fog” are also common, as thyroid hormones play a critical role in brain function.
On the other hand, hyperthyroidism, or an overactive thyroid, happens when the gland produces too many hormones. This can lead to rapid heartbeat, unintentional weight loss, increased appetite, excessive sweating, and difficulty sleeping. Anxiety, irritability, and tremors may also occur, reflecting the hormone’s effect on the nervous system.
Other thyroid issues include goiter (an enlarged thyroid), thyroid nodules, and autoimmune disorders such as Hashimoto’s thyroiditis and Graves’ disease. These conditions can cause a mix of symptoms or remain silent until discovered during a routine checkup.
Because symptoms can be gradual or mimic other health issues, it’s important to pay attention to persistent changes in your body. If you notice unusual fatigue, weight fluctuations, mood swings, or changes in hair or skin, consider speaking with a healthcare professional. Early detection and treatment can help restore balance, improve quality of life, and prevent long-term complications.
Causes of Thyroid Problems
Thyroid problems can develop for a variety of reasons, ranging from genetic factors to lifestyle influences. One of the most common causes is autoimmune disorders, where the immune system mistakenly attacks the thyroid. Conditions like Hashimoto’s thyroiditis often lead to hypothyroidism, while Graves’ disease typically results in hyperthyroidism. These autoimmune responses disrupt normal hormone production and can affect overall health.
Another key factor is iodine imbalance. Iodine is essential for thyroid hormone production. Too little iodine can lead to hypothyroidism and goiter, while excessive iodine intake may trigger hyperthyroidism in sensitive individuals. In some cases, dietary deficiencies in selenium, zinc, or iron can also impair thyroid function.
Genetics play a role as well. A family history of thyroid disease increases the likelihood of developing thyroid issues, particularly autoimmune-related disorders.
Lifestyle factors such as chronic stress, poor diet, and exposure to environmental toxins can influence thyroid health. Stress affects hormone balance, potentially altering TSH levels and thyroid hormone production. Certain medications, including lithium and amiodarone, can also impact thyroid function.
Finally, age and gender matter. Women, especially during pregnancy or menopause, are more prone to thyroid disorders, while the risk of thyroid dysfunction generally increases with age.
Understanding these causes is crucial because it helps you identify risk factors and take preventive measures. In the next sections, we’ll explore how thyroid issues are diagnosed and the treatments available to restore balance and improve overall health.
Diagnosing Thyroid Issues
Detecting thyroid problems early is essential for maintaining overall health, but because symptoms can be subtle or mimic other conditions, proper testing is crucial. The first step in diagnosis usually begins with a medical evaluation. During a physical exam, a doctor may feel your neck for enlargement, nodules, or irregularities in the thyroid gland. They’ll also review your medical history and symptoms to determine if further testing is needed.
The most common method for confirming thyroid function is a blood test. Key tests include TSH (thyroid-stimulating hormone), which indicates how well your thyroid is being regulated by the pituitary gland, and T3 and T4 levels, which measure the actual thyroid hormones in your bloodstream. Abnormal results can indicate an underactive or overactive thyroid. Additional blood tests may measure thyroid antibodies, which help identify autoimmune conditions like Hashimoto’s thyroiditis or Graves’ disease.
In some cases, imaging tests may be recommended. An ultrasound can detect nodules, cysts, or enlargement of the gland, while a radioactive iodine uptake scan can assess how effectively your thyroid is producing hormones.
Accurate diagnosis allows healthcare providers to tailor treatment plans to your specific condition, whether it’s hormone replacement, medication, or lifestyle interventions. Because thyroid imbalances affect metabolism, energy, and many bodily systems, timely evaluation is critical.
If you notice persistent fatigue, unexplained weight changes, or other related symptoms, it’s important to consult a healthcare professional. Proper testing ensures you get the right treatment and maintain optimal thyroid health.
Treatment Options for Thyroid Disorders
Treating thyroid problems depends on whether the gland is underactive, overactive, or affected by another condition. For hypothyroidism (underactive thyroid), the most common treatment is thyroid hormone replacement therapy. Doctors typically prescribe levothyroxine, a synthetic form of T4, to restore hormone levels and normalize metabolism. With proper dosing, most people experience improved energy, weight management, and overall well-being. Regular blood tests are important to ensure hormone levels remain balanced.
For hyperthyroidism (overactive thyroid), treatment focuses on reducing excessive hormone production. Medications such as methimazole or propylthiouracil can help slow hormone synthesis. In more severe cases, radioactive iodine therapy may be used to shrink overactive thyroid tissue, or surgery (thyroidectomy) may be necessary to remove part or all of the gland. Beta-blockers are sometimes prescribed to manage symptoms like rapid heartbeat and tremors.
Ongoing monitoring is crucial for all thyroid conditions. Because hormone levels fluctuate, patients need regular checkups and blood tests to adjust treatment as needed. Lifestyle measures, including a nutrient-rich diet, stress management, and regular exercise, can support medical treatments and help maintain thyroid balance.
It’s important to note that self-diagnosis or altering medications without medical guidance can be dangerous. Consulting a healthcare professional ensures proper treatment and prevents complications. With timely intervention and consistent care, most thyroid disorders can be effectively managed, allowing individuals to maintain energy, mental clarity, and overall health.
Supporting Thyroid Health Naturally
While medical treatment is essential for diagnosed thyroid disorders, there are several natural ways to support thyroid function and overall health. Nutrition plays a key role. The thyroid requires specific nutrients, including iodine, selenium, and zinc, to produce hormones effectively. Foods such as seaweed, fish, eggs, Brazil nuts, and whole grains can help supply these essential nutrients. However, it’s important not to overconsume iodine, as excess can also disrupt thyroid function.
Lifestyle habits also influence thyroid health. Regular exercise helps boost metabolism and maintain healthy body weight, while stress management techniques—like meditation, yoga, or deep breathing—can prevent hormone imbalances caused by chronic stress. Adequate sleep is another critical factor, as it supports overall hormonal balance and energy levels.
Avoiding environmental toxins and excessive consumption of processed foods can also protect thyroid function. Certain foods, known as goitrogens—such as raw cruciferous vegetables (broccoli, cauliflower, cabbage)—may interfere with hormone production in sensitive individuals, so moderation is key.
Supplements should be approached cautiously and only under a doctor’s guidance. For example, iodine and selenium supplements can be beneficial for some people but harmful for others, depending on their thyroid condition.
By combining nutrient-rich foods, healthy lifestyle choices, and mindful supplementation when necessary, you can support your thyroid’s natural function. These proactive steps can enhance energy, metabolism, and overall well-being, complementing any medical treatment prescribed for thyroid disorders.
Thyroid and Overall Health
The thyroid plays a crucial role in maintaining overall health because its hormones affect nearly every system in the body. One of its primary functions is regulating metabolism, which determines how efficiently your body converts food into energy. When thyroid function is balanced, energy levels are stable, weight is easier to manage, and daily activities feel less exhausting. Conversely, an underactive thyroid can slow metabolism, causing fatigue and weight gain, while an overactive thyroid can accelerate metabolism, leading to weight loss and rapid heartbeat.
Thyroid hormones also significantly impact mental health and mood. An imbalance can contribute to anxiety, depression, irritability, or brain fog. Adequate thyroid function is essential for cognitive function, memory, and focus, highlighting its role in everyday productivity.
In addition, the thyroid affects the cardiovascular system, influencing heart rate and blood pressure. It supports muscle strength, bone health, and digestive function, and even contributes to reproductive health and menstrual cycle regulation in women.
Because the thyroid influences so many systems, an untreated imbalance can have widespread consequences. Fatigue, weight changes, mood swings, and sleep disturbances are often early warning signs that shouldn’t be ignored.
Maintaining thyroid health through proper diagnosis, treatment, nutrition, and lifestyle habits is essential for long-term well-being. Supporting your thyroid can lead to improved energy, better mood, enhanced metabolism, and overall vitality, demonstrating just how interconnected this small gland is with your entire body.
FAQs About Thyroid Health
1. Can thyroid problems affect weight?
Yes, thyroid hormones regulate metabolism, so an underactive thyroid (hypothyroidism) can slow metabolism and lead to weight gain, while an overactive thyroid (hyperthyroidism) can accelerate metabolism and cause weight loss.
2. How do I know if my thyroid is underactive or overactive?
Symptoms can provide clues. Hypothyroidism often causes fatigue, cold intolerance, dry skin, constipation, and weight gain. Hyperthyroidism may cause rapid heartbeat, anxiety, heat intolerance, excessive sweating, and weight loss. Blood tests are required to confirm the condition.
3. Is thyroid disease hereditary?
Genetics can play a role. A family history of thyroid disorders increases your risk, particularly for autoimmune conditions like Hashimoto’s thyroiditis and Graves’ disease.
4. Can lifestyle changes improve thyroid function?
While lifestyle changes cannot replace medical treatment, they can support thyroid health. Eating a nutrient-rich diet, managing stress, getting enough sleep, and exercising regularly can help your thyroid function optimally.
5. How is thyroid disease diagnosed?
Thyroid function is diagnosed through blood tests measuring TSH, T3, T4, and sometimes thyroid antibodies. Imaging tests, like ultrasounds, may be used to detect nodules or enlargement.
6. Can untreated thyroid problems affect overall health?
Yes. Thyroid imbalances can impact metabolism, energy, mood, heart health, digestion, and even cognitive function. Early diagnosis and treatment are essential to prevent complications and maintain overall health.
7. Should I take supplements for thyroid health?
Supplements like iodine or selenium may help some individuals, but they should only be taken under a doctor’s guidance to avoid worsening thyroid problems.
Conclusion:
The thyroid may be small, but its impact on your body is enormous. This butterfly shaped gland regulates metabolism, energy levels, heart rate, mood, digestion, and even brain function.
When functioning properly, it helps you feel balanced, energized, and focused. However, when the thyroid is out of balance if underactive or overactive it can lead to a wide range of symptoms, including fatigue, weight changes, mood swings, and cognitive challenges.
Understanding the thyroid’s role is the first step toward recognizing potential issues. Early detection through blood tests and physical examinations can make a significant difference in managing thyroid disorders effectively.
Treatments, ranging from hormone replacement therapy to medications for overactive thyroid, can restore balance and improve quality of life.
Alongside medical interventions, supporting your thyroid naturally through a nutrient rich diet, regular exercise, stress management, and adequate sleep can further optimize its function.
Being mindful of symptoms and proactive about your health allows you to maintain your energy, metabolism, and overall well-being.
Ultimately, the thyroid is a powerful but often overlooked gland that touches almost every aspect of your health. By understanding its functions, recognizing signs of imbalance, and taking steps to support it, you can keep your thyroid and your body functioning at its best.
Your small gland truly makes a big difference, so caring for it is an investment in your long term health and vitality.